Get a quote, configure a custom safety solution or ask a question. We're here to help!








- Spill ContainmentMore …Loading Safety CagesMore …
SafeRack Worldwide
We pride ourselves on one-on-one customer service. When you call SafeRack, we'll be there to answer your questions with a combined experience of 400+ years.
Select your region below.- View Products
- Railcar & Truck Loading Platforms
- Gangways & Loading Ramps
- Stairs, Platforms & Ladders
- Mobile Ladders & Platforms
- Loading Arms & Fluid Transfer
- Safety Gates & Traffic Control
- Aviation & Aerospace Access
- Marine Access & Loading
- Grounding & Monitoring
- Spill Containment
- Loading Safety Cages
- Transloaders & Skids
- Shelters & Canopies
- Fall Protection
- Terminal & Speciality
Home / Industries / Bulk Chemical Loading / Phenol Handling Design, Loading, and Installation.Phenol (C6H5OH) Handling Design, Loading, and Installation.
Phenol is used primarily in the production of phenolic resins and in the manufacture of nylon and other synthetic fibers.
What is Phenol? Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula of C6H5OH. A mildly acidic toxic white crystalline solid obtained from coal tar and used in chemical manufacturing. In a diluted form, under the name of carbolic acid, it’s used as a disinfectant. Due to its acidic properties, Phenol requires careful handling due to its likelihood to cause chemical burns.
In the United States, Phenol is a “tight-fill” (closed-loop) loading operation and is loaded into road tankers and rail cars via chemical hoses or top loading arms with vapor recovery. Phenol, if not handled properly can be fatal therefore Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is required. Additionally, because operators are on top of the vehicles during the loading process, fall prevention is essential, not only for safety but increases throughput.


















Question, Get a Quote, Live Demo or Request an On-Site Visit
Our experts simplify the complex
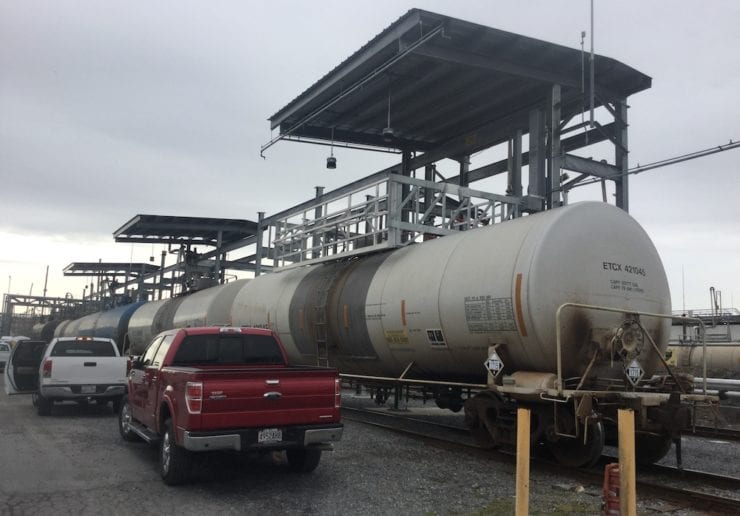
View Full TextPhenol is typically transported in DOT 103 general service tank cars or approved DOT trailers include MC 300 thru MC 312 , MC 330 and MC 331.
Phenol is typically transported in a molten state via insulated, DOT 103 general service tank cars with safety valves. The rails cars themselves are 9′ outside diameter with an overall length of ~47′, with a 6’ x 6′ or 8’ x 8’ centered crash box.
Tank truck (un)loading procedures are similar to railcar applications with the trailers meeting established DOT requirements for hauling phenol or similar commodities.
Approved DOT trailers include MC 300 thru MC 312 , MC 330 and MC 331. All trailers must be equipped with pressure relief valves; and trailers with bottom outlets must be equipped with remote-controlled stop valves.
Loading Arms
Generally speaking, SafeRack recommends rigid pipe loading arms where possible for the following reasons:
- Balanced throughout their movement envelope
- Designed not to hit the ground – protecting the asset and the operator
- Ergonomic – one man operation
- Fitted with manual or actuated valves.
- Fitted with optional purge/vent facilities
- Can be moved into position with ease and left hanging in the air while the operator prepares the tanker connection
- Parked neatly
Hoses require:
- Annual pressure test
- Are difficult to stow neatly when not in use
- Can be dropped
- Can be driven over
- Are very heavy to use if fitted with a valve at the tanker connection point
- Cannot be easily heated or have vent/purge valves fitted to it
- Prone to catastrophic failure
Loading Arms
Generally speaking, SafeRack recommends rigid pipe loading arms where possible for the following reasons:
- Balanced throughout their movement envelope
- Designed not to hit the ground – protecting the asset and the operator
- Ergonomic – one man operation
- Fitted with manual or actuated valves.
- Fitted with optional purge/vent facilities
- Can be moved into position with ease and left hanging in the air while the operator prepares the tanker connection
- Parked neatly
Hoses require:
- Annual pressure test
- Are difficult to stow neatly when not in use
- Can be dropped
- Can be driven over
- Are very heavy to use if fitted with a valve at the tanker connection point
- Cannot be easily heated or have vent/purge valves fitted to it
- Prone to catastrophic failure
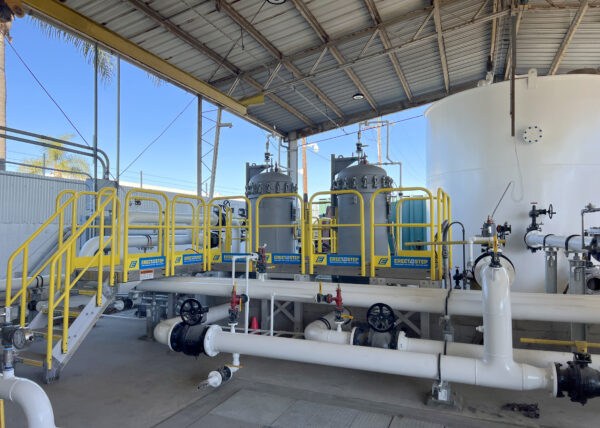
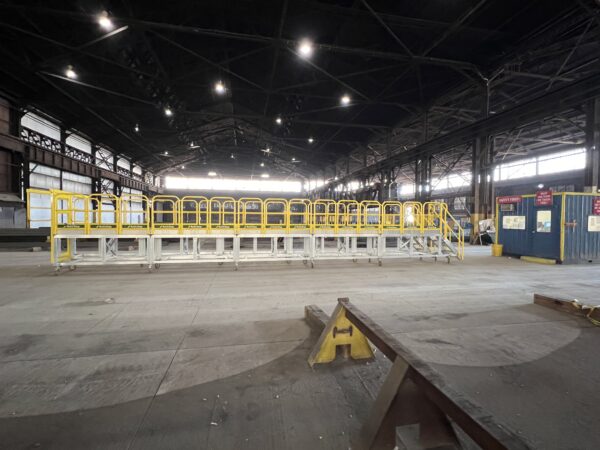
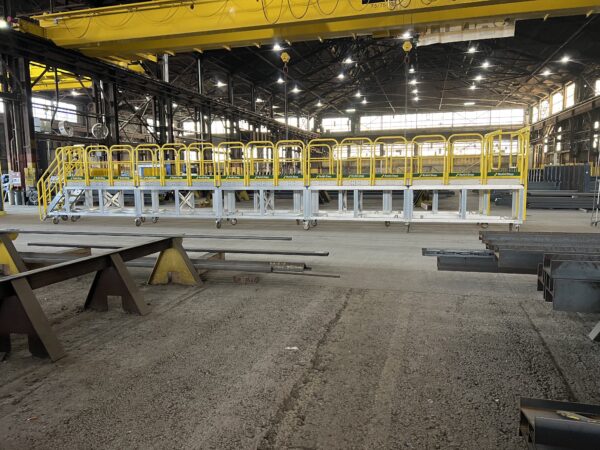
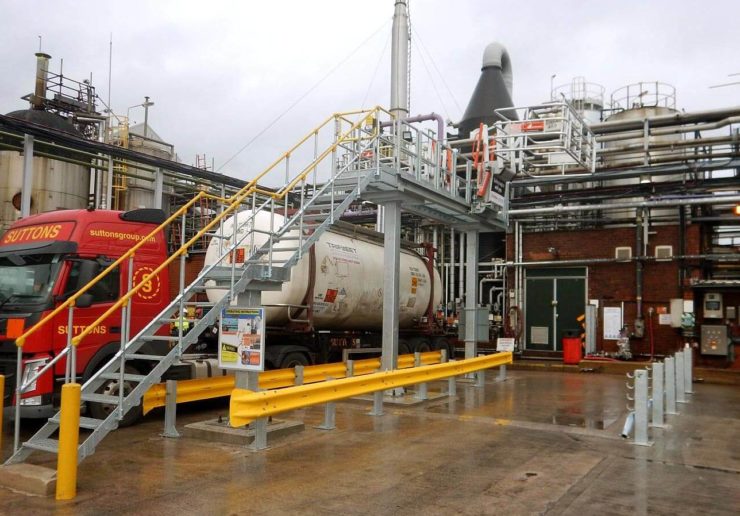
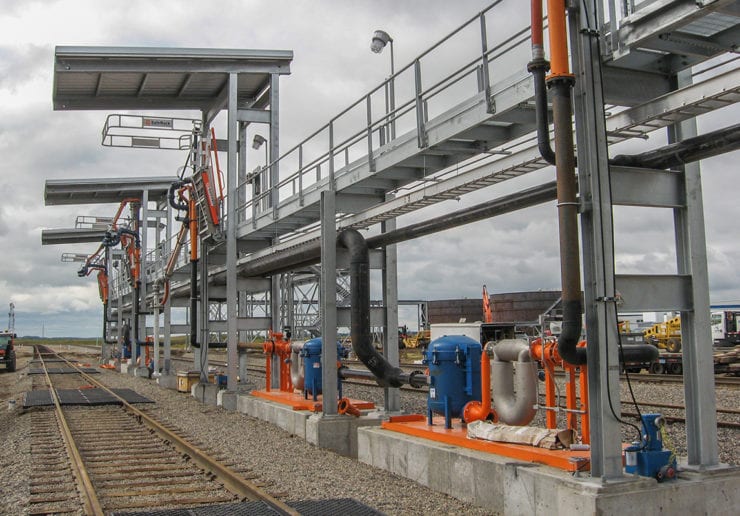
Typical Phenol Loading Platform
Quote or discuss your installation.
Start by selecting loading application"*" indicates required fields
Below are some of the loading and unloading solutions for illustrative purposes only. Our experts will work with you and your team for a custom solution to suit your needs.
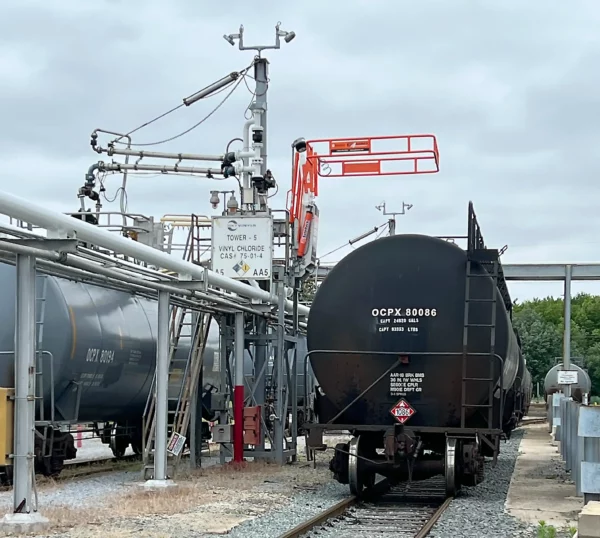
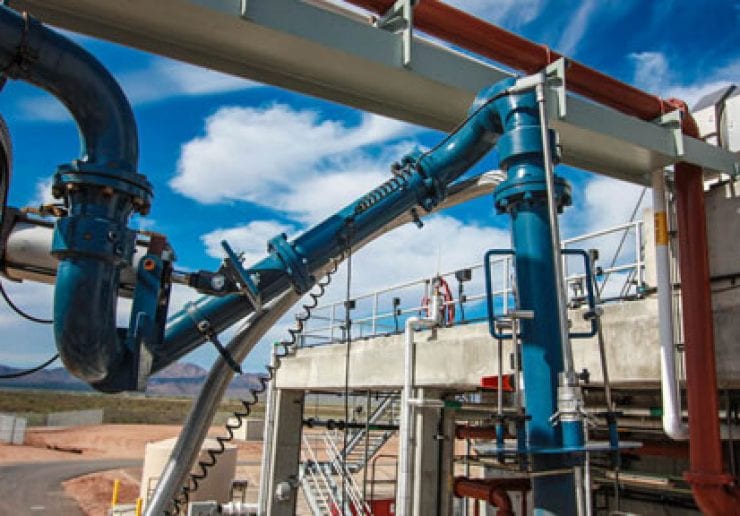
Phenol Loading Arms

Phenol is typically loaded into railcars via chemical hoses or loading arms. The current best loading practice is to use a 3″ chemical hose or a stainless steel loading arm with quick-acting coupling, often in the form of Hammer Unions with stabber pipe. The hose or arm will have a top inlet with a control valve to ensure that it is self-draining after use and is supported along the length of a mechanical loading arm to improve handling; this is known as a by-pass arm. You can install one liquid and one vapor arm, or mount both the liquid and vapor hoses on one by-pass arm.
Break-away couplings can be fitted near the inlet of the hose for additional safety in the event of a premature departure.
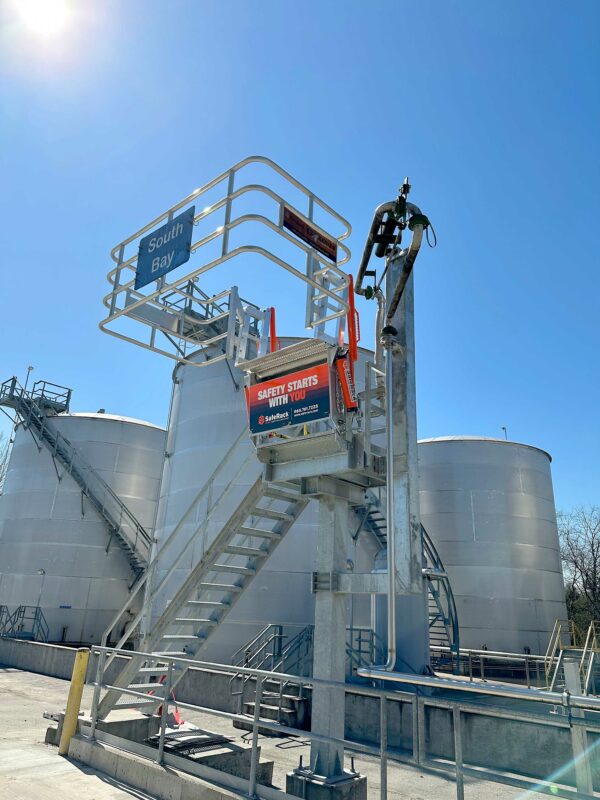
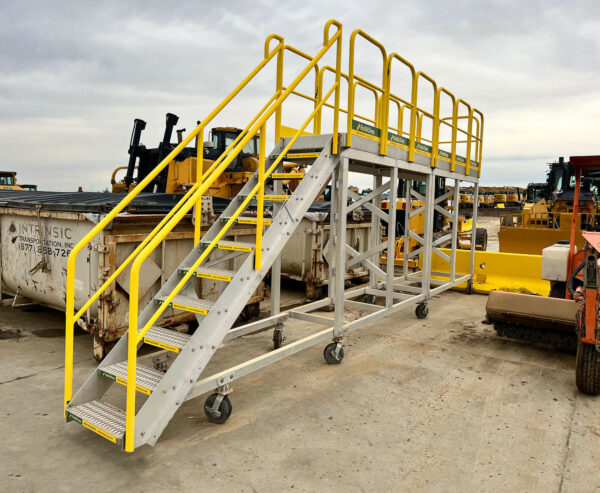
Phenol Loading Gangways and Safety Cages

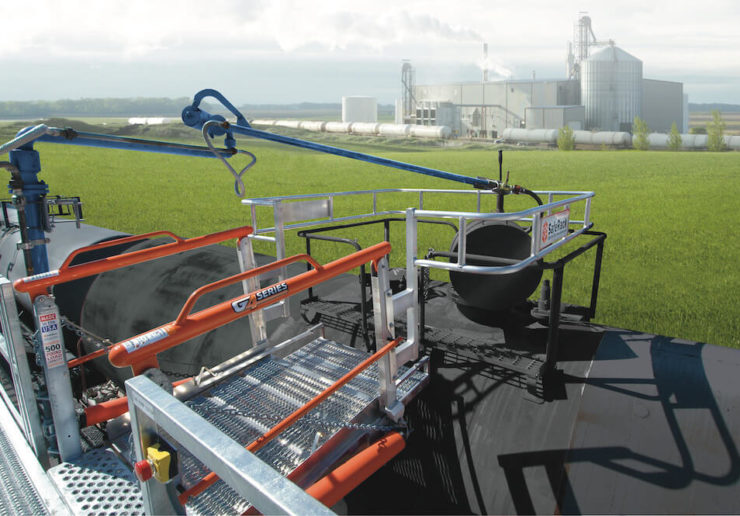
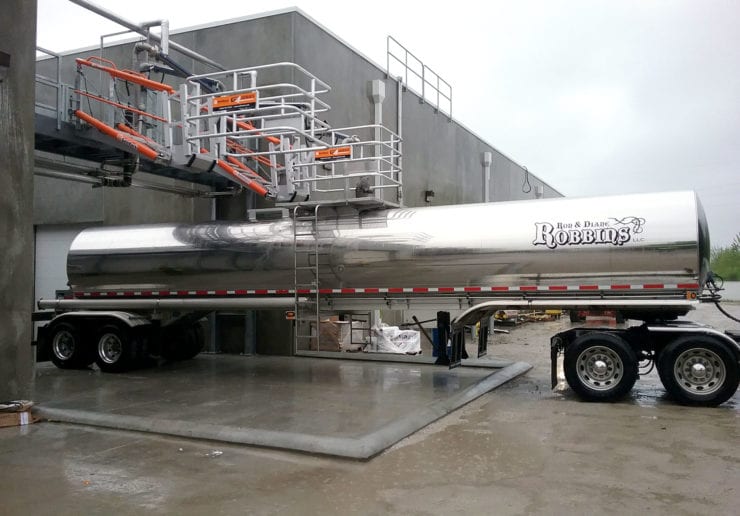
A wider access gangway (36″-48″ is preferable) as it helps improve access and egress to and from the vessel. In addition, a wider gangway will reduce the risk of the operator’s PPE getting caught, torn or damaged, and will improve productivity and safety. Powered gangway solutions are also an option, with both hydraulic and pneumatic solutions being commonly used. Each gangway will be fitted with a two-rail safety cage for the railcar crash box. This will be a centered 6’x6’ safety cage to sit directly over the cashbox. This will provide a safe, secure work environment for your operator when connected to their breathing apparatus.

SafeRack’s GX SAS gangways use Retractalok power-assist technology allowing operators to raise or lower effortlessly, light as a feather to lift, and solid as a rock. Tested in the most critical applications, this revolutionary new gangway outperforms all others. Available in multiple lengths and widths.
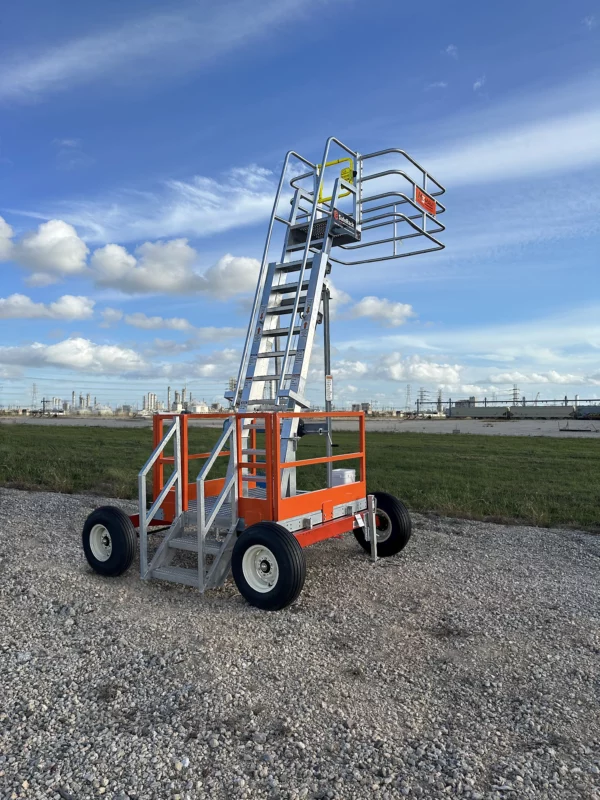
Learn MoreMAXRack Elevating Safety Cage
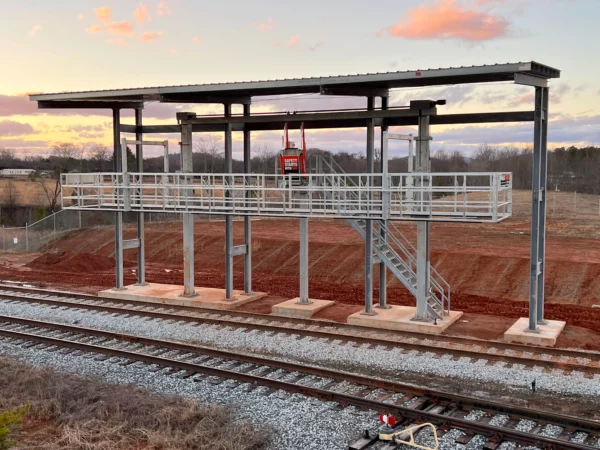
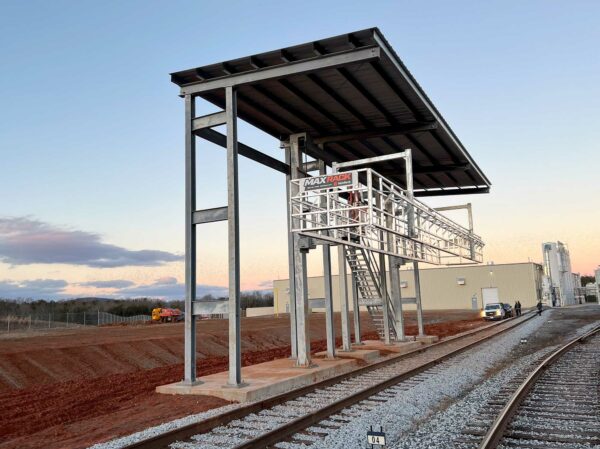
 As an alternative to our two and four-rail safety cages, some customers prefer our MAXRack elevating safety cages. The ultimate fall prevention solution engineered to keep operators safe and productive. Designed for both trucks or railcars, and available in multiple cage lengths and widths. Safe, durable, and easy to use. MAXRack is built rock-solid with galvanized steel column supports and lifting arms (cages can be Aluminum, Galvanized, or Stainless Steel depending on application) Available in two power options – Pneumatic Air Drive and Electric Drive (Explosion and Non-Explosion Proof).
As an alternative to our two and four-rail safety cages, some customers prefer our MAXRack elevating safety cages. The ultimate fall prevention solution engineered to keep operators safe and productive. Designed for both trucks or railcars, and available in multiple cage lengths and widths. Safe, durable, and easy to use. MAXRack is built rock-solid with galvanized steel column supports and lifting arms (cages can be Aluminum, Galvanized, or Stainless Steel depending on application) Available in two power options – Pneumatic Air Drive and Electric Drive (Explosion and Non-Explosion Proof).
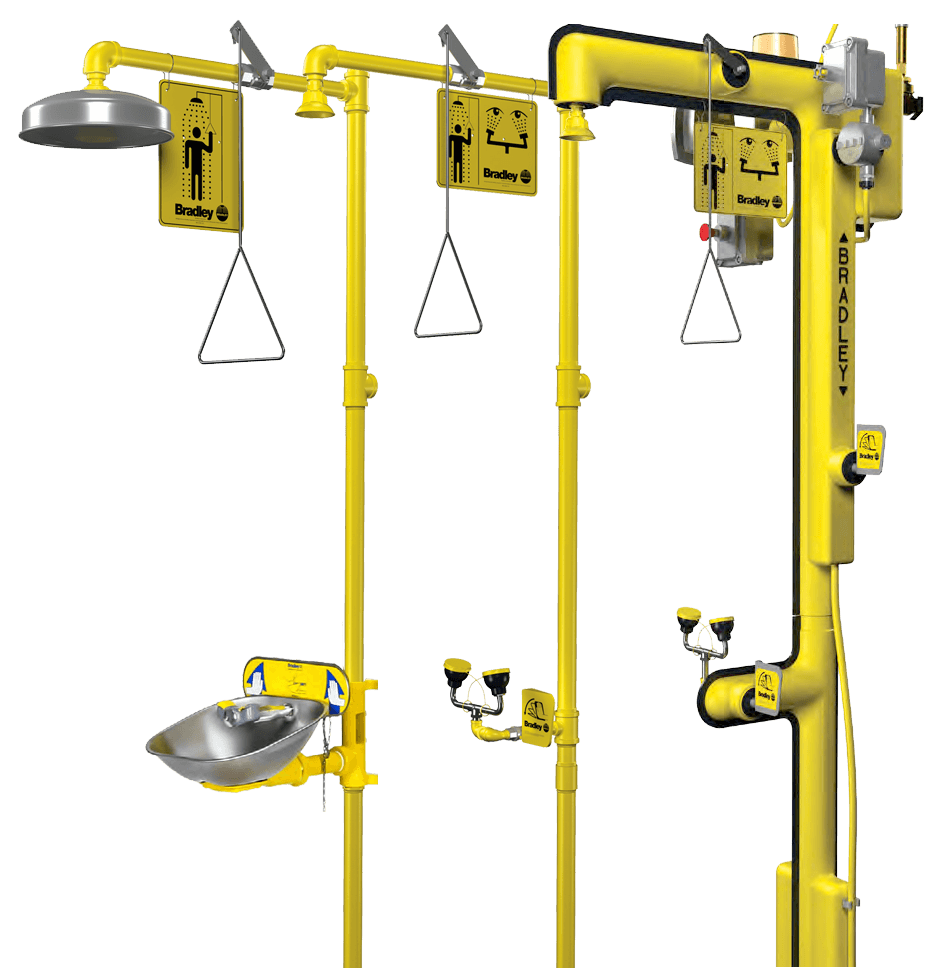
Learn MorePhenol Eye Wash/Drench Showers

ANSI guidelines state that an Eye Wash/Drench Showers need to be located 10 seconds or 55’ (16.8m) from contaminants or hazardous materials. Eyewash stations need to be on the same horizontal plane with no obstructions.
Therefore, we would propose the installation of a standard combination Drench Shower/Eyewash Unit, which will save limited space and fit easily into any work
Phenol Spill Containment

Spill containment pans will be provided at the point of loading operations and is an essential piece of equipment in overall site safety and environmental protection Phenol Grounding

Phenol is highly flammable, and industry best practice includes the grounding of all vessels before starting the (un)loading process. - Vehicle grounding and bonding — ensure true grounding before product flow is permitted
- Explosion-proof enclosures — meet or exceed UL, CSA and Ex requirements
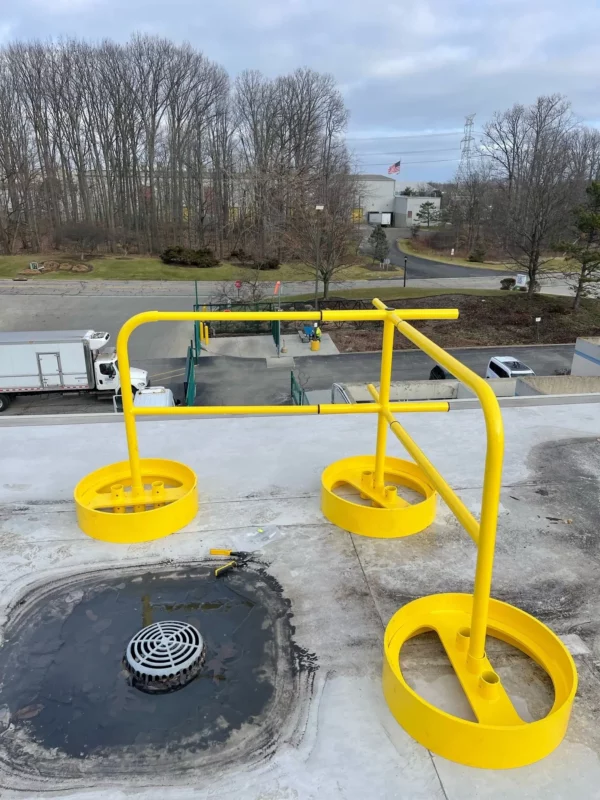
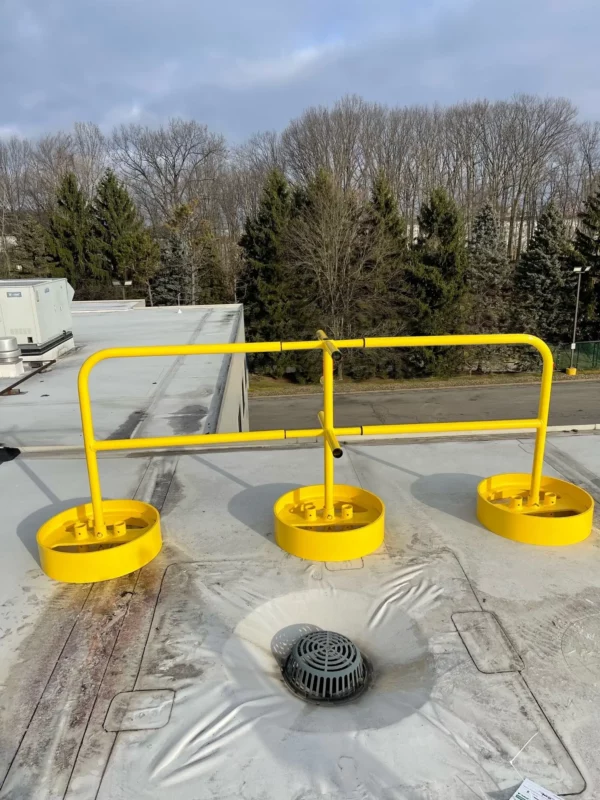
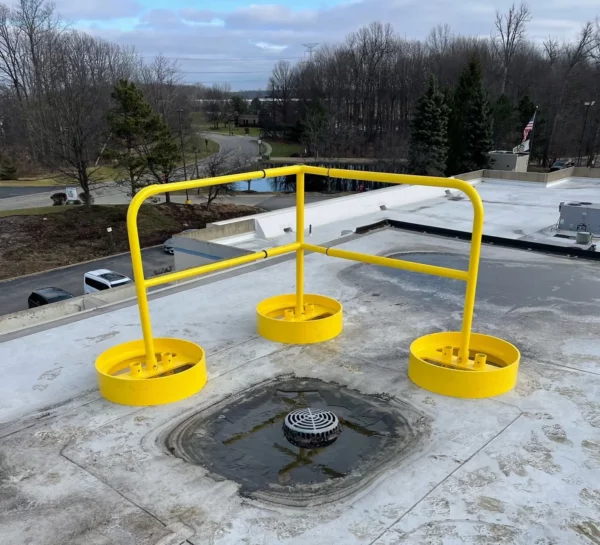
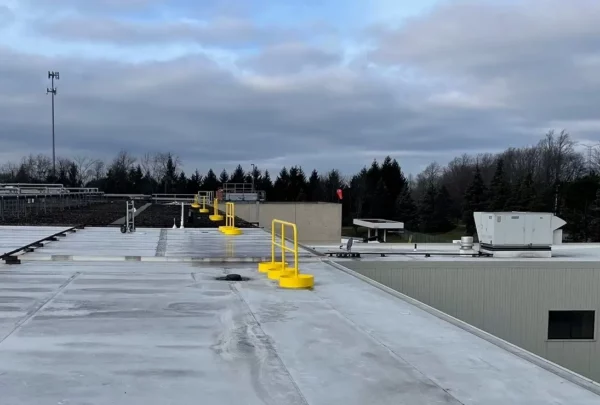
Phenol Safety Gates

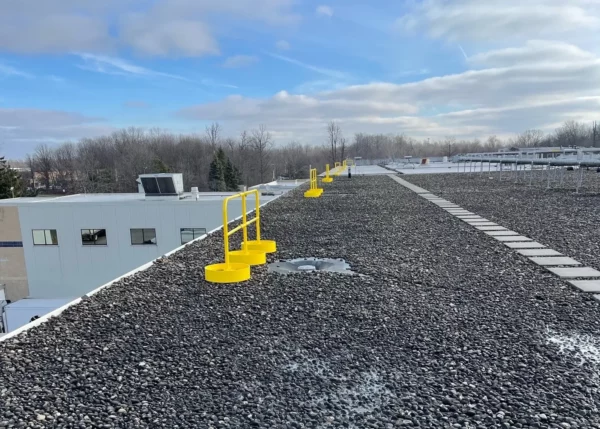
Safety Gates will be installed at the top of stairs and any other openings to ensure operator safety at all times.  YellowGate Safety Gates
YellowGate Safety GatesSafeRack’s line of industrial safety gates is the most flexible product on the market with the ability span openings between 16” and 36” and is field adjustable with nothing more than a wrench. Learn More
Phenol Options

- Lighting – Lighting both over and under the platform will be provided. For overcast days or second shift, lighting is essential for improved safety and improved productivity.
- Platform & Canopies – Full platform canopies reduce exposure to the elements and improve the safe and productive loading operation from the operator’s perspective.
- Operator Shelter – Depending on your site requirements, consideration should be given to the requirement of an operator or guard building on the loading platform. This can be customized to meet specific site requirements
- Wheel Chocks – Railcar Wheel Chocks provide fast blocking of all types of railcars and meet OSHA regulations to safely prevent railroad cars from moving during loading or unloading operations. This is a requirement by the Department of Homeland Security
Personal Protective Equipment PPE Requirements
Eye/Face Protection: Wear chemical safety goggles. A face shield (with safety goggles) may also be necessary.
Skin Protection: Wear chemical protective clothing e.g. gloves, aprons, boots. Coveralls or long sleeve shirts and pants in some operations. Wear a chemical protective, full-body encapsulating suit, and self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). Suitable materials include: butyl rubber, neoprene rubber, Viton®, Viton®/butyl rubber, Barrier® – PE/PA/PE, Silver Shield® – PE/EVAL/PE, Trellchem® HPS, Trellchem® VPS, Saranex®™, Tychem® BR/LV, Tychem® Responder® CSM, Tychem® TK. The following materials should NOT be used: natural rubber, polyvinyl chloride. Recommendations are NOT valid for very thin neoprene rubber gloves (0.3 mm or less).
Respiratory Protection: Up to 5 ppm:
(APF = 10) Any chemical cartridge respirator with cartridge(s) providing protection against Phenol*; or Any supplied-air respirator*.
*Reported to cause eye irritation or damage; may require eye protection.
APF = Assigned Protection Factor
Recommendations apply only to National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) approved respirators. Refer to the NIOSH pocket guide to chemical hazards for more information.
Use a local exhaust ventilation and enclosure, if necessary, to control the amount in the air. Consider using a corrosion-resistant exhaust ventilation system separate from other ventilation systems. It may be necessary to use stringent control measures such as process enclosure to prevent product release into the workplace. Use backup controls (e.g. double mechanical pump seals) to prevent the release of this material due to equipment failure. * For illustrative purposes only. Our experts will work with you and your team for a custom solution to suit your needs Phenols are also used in household products and as intermediates for industrial synthesis. For example, phenol in low concentrations is used as a disinfectant in household cleaners, and even in mouthwashes. Phenol may have been the first surgical antiseptic. Phenol can be very dangerous, and the hazards are not just those of a typical corrosive. The dangers of phenol are two-fold. It’s both a corrosive (can cause severe burns) and a toxic (if absorbed phenol acts as a systemic toxin). Death was reported from the ingestion of as little as 15ml. Again, the primary hazard of phenol is its ability to penetrate the skin rapidly, causing severe burns, and its toxicity even in small amounts. Due to its local anesthetizing properties, skin burns may be painless.
Phenol is considered a Category 4 flammable liquid by OHSA and has a flashpoint of 79 degrees C and 174 degrees F. During a fire, phenol may decompose into hazardous carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Phenol doesn’t work well with most metals, rubber, plastics, or alloys.

Helping a chemical company access their tanker truck Phenol is typically loaded (tight-fill) into the tops of rolling stock/tank trucks and unloaded from the bottom. Variations on the preferred method of loading include a close dome, tight fill, splash fill with cover plate and vapor recovery, and tight fill with dry break couplers.
Best practices for phenol loading/unloading include: wearing a chemical suit, rubber gloves, splash goggles, face shield, rubber boots, and a self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). Because operators are regulated to wear a restrictive chemical suit, SafeRack suggests the use of a wider gangway and a MAX Rack for more ergonomic access and egress. A wider gangway will reduce the risk of the operator’s PPE getting caught, torn, or damaged, as well as address offset crash boxes.
To protect operators, SafeRack offers numerous options for fall prevention safety cages, including- two, three, and four rail designs.
Best practice includes the grounding of all vessels before starting the (un)loading process. For overcast days or second shift, lighting is an inexpensive and is essential for safety and improved productivity. Safety showers and eyewash stations should have alarms to alert workers of possible exposure.
SafeRack understands that accidents can happen. Properly equipping your loading terminal with rail or truck spill containment will save costly cleanup, downtime, and EPA/OSHA fines. In the event of a chemical release or spill, operators need to stay upwind. Having a windsock on your platform provides a visual reference to help keep workers out of harm’s way in the event of an emergency.
Phenol is a mildly acidic toxic white crystalline solid obtained from coal tar and used in chemical manufacture and a diluted form (under the name carbolic) as a disinfectant. Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C6H5OH. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. It’s mildly acidic and requires careful handling due to its likelihood to cause chemical burns.
Phenol can be tasted and smelled at levels lower than those associated with harmful effects. Phenol evaporates slower than water and can form a solution with water. Primarily, phenol is used in the production of phenolic resins and the manufacture of nylon and other synthetic fibers.
Servicing all areas of bulk chemical industries
SafeRack has developed industry-leading safe access solutions, seamlessly integrating loading arms and ancillary 3rd party equipment to be user friendly with the operation of (un)loading becoming cleaner, more automated, and far safer.
Petrochemicals are made from either petroleum or natural gas feedstock. A wide variety of petrochemicals are created/produced depending on the process.
- Aromatics – Aromatics are hydrocarbons that consist exclusively of the elements carbon and hydrogen. Common Aromatics are Benzene, Toluene, and Xylenes. Often used for creating Dyes, synthetic detergents, fibers, and plastics.The catalytic reforming of naphtha produces aromatics, which include benzene, toluene, and xylene. Together they are referred to as BTX and are predominantly obtained from petroleum refineries by the extraction from the reformate produced in catalytic reformers using naphtha obtained from petroleum refineries.
- Olefins – The most reactive class of hydrocarbons tend to crack. Common Olefins are Ethylene, Propylene, and Butadiene. Often used for creating plastics, and synthetic rubber. Chemical plants produce olefins by steam cracking of natural gas liquids like ethane and propane. Olefins include ethene, propene, and butadiene. Ethylene and propylene are chief sources of both plastic products and industrial chemicals. Butadiene is mainly used in the production of synthetic rubber.
- Synthesis gas (SynGas) – A mixture comprising of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen. Common Synthesis Gas is Ammonia and Methanol. Often used for creating Fertilizers and explosives. Synthesis gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen used to make ammonia and methanol. Ammonia is used to make the fertilizer urea, and methanol is used as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Steam crackers are not to be confused with steam reforming plants used to produce hydrogen and ammonia.

Phenol 101
Things to know about Phenol
Phenol is regulated by the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and is classified as a toxic, corrosive, and flammable substance, with the DOT identification number UN 2821.
Phenols are used in household products and as intermediates for industrial synthesis. For example, phenol in low concentrations is used as a disinfectant in household cleaners, and even in mouthwashes. Phenol may have been the first surgical antiseptic.
Phenol is considered a Category 4 flammable liquid by OHSA, and has a flashpoint of 79 degrees C and 174 degrees F. During a fire phenol may decompose into hazardous carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.

Phenol can be very dangerous, and the hazards are not just those of a typical corrosive. The hazards of phenol are two (2) fold. It’s both a corrosive (can cause severe burns) and a toxic (if absorbed phenol acts as a systemic toxin). Death can result from the ingestion of as little as 15ml.
Again, the major hazard of phenol is its ability to penetrate the skin rapidly, causing severe burns, and its toxicity even in small amounts. Due to its local anesthetizing properties, skin burns may be painless.
Best practice in handling Phenol includes operators wearing chemical suits, rubber gloves, splash goggles, face shields, rubber boots, and a self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA).
Safety showers and eyewash stations should also have alarms to alert workers of possible exposure.
Phenol doesn’t react well with most metals, rubber, plastics, or alloys. Therefore, stainless steel is the recommended material of construction for process piping etc.
Customer Reviews
 5 5We needed a replacement part and it was in stock and ready to ship
5 5We needed a replacement part and it was in stock and ready to shipOur metal gangway needed a replacement spring. SafeRack made sure we received it quick.
By Ray Smerdon from Engineered Systems Inc on 1/23/20 5 5We are very pleased with our ErectaStep Platform System
5 5We are very pleased with our ErectaStep Platform SystemGreat communication, updates, and customer service.
By Bob Cannon from Enterprise Products Partners on 3/16/20 5 5User friendly and SAFE!
5 5User friendly and SAFE!User friendly and SAFE! Well built and built to customers needs. The quote was received in a timely matter. The sales team was friendly and professional. The unit is built well and to our exact needs.
By Kyle Ammann from Glacial Lakes Energy LLC on 10/2/14 5 5This is a solid product that we will use for years.
5 5This is a solid product that we will use for years.Product was delivered at the specified time. Your team was very helpful in fitting the install within the project demands. The overall fit and finish is excellent. The best part is that we now feel that fall protection is not an issue at the site anymore. Stephen was good to work with – he kept us on track. The site visit ensured we got what we needed and gave us comfort as we moved forward in the project. We can tell this is a solid product that we will use for years.
By Sam Hinson from RPM Wood Finishes Group on 1/4/17 5 5Safe Access Gangway
5 5Safe Access GangwayYou guys were able to meet our need for expedited shipping and produced three-fold downs and had them out the next day in order for us to complete a project. That was outstanding.
By T. Hart from Fall Protection Systems on 6/26/20 5 5All positive experiences! Even my customer agreed!
5 5All positive experiences! Even my customer agreed!My salesman Joe Free was fantastic, he was incredibly responsive & was very honest with me when it came to what my customer really needed for their application. As I could not be there for the on-site visit – my customer was drawn to a new unit from SafeRack as they already had a unit they were using & liked, recommended by their safety manager, lead times were short & installation is easy!
By Kelsey Ihle from Dival Safety Equipment Inc. on 12/26/18
Is your plant or facility compliant with ANSI, OSHA, and local safety codes? We can help!


EMERGENCY EYEWASHES / SHOWER EQUIPMENT AND THE ANSI/ISEA Z358.1 – 2014 STANDARD
Following eye contact, you must start washing with water immediately to prevent permanent damage. In the event of skin contact, you must start washing with water immediately to prevent slow-healing chemical burns.
Are you aware that ANSI guidelines state that Eye Wash/Drench Showers need to be located 10 seconds or 55′ from contaminates or hazardous materials and located on the same horizontal plane, with no obstructions? If bottom loading/unloading, an additional shower should be located at grade as well. SafeRack provides the above equipment plus much more needed to keep employees safe and expedite bulk chemical loading and unloading.
OSHA Regulation Experts – Does your existing chemical safety equipment or chemical loading systems meet OSHA’s latest requirements? SafeRack’s professional technical sales consultants are available to meet with your team to make recommendations to keep your facility in front of OSHA’s ever-changing country and region-specific standards and regulations, including lifeline and trolley beam fall arrest systems, metal stairs, and access platforms.
Why SafeRack?
The SafeRack approach is a collaborative one. Let’s call it The SafeRack Way. We have, over many years amassed a great deal of experience and understanding of the safety aspects involved in loading road tankers and railcars, as well as the behavioral habits of the operators.

Experts In Chemical Loading
- Acetic Acid
- Acetic Anhydride
- Acetonitrile
- Acrolein
- Acrylic Acid
- Acrylonitrile
- Aluminum Chloride
- Aluminum Sulfate
- Ammonia
- Ammonium Hydroxide
- Ammonium Nitrate
- Aniline
- Benzene
- Benzyl Chloride
- Bromotrifluoromethane
- Butadiene
- Carbon Dioxide
- Caustic
- Chlorine
- Chloroform
- Chlorosulfonic Acid
- DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid)
- Diethylene Glycol
- Dimethylformamide
- Dodecylbenzene Sulfonic Acid
- Ethanol
- Ethyl Acetate
- Ethyl Chloride
- Ethylene
- Ethylene Dichloride
- Ethylene Glycol
- Ethylene Oxide
- Ferric Chloride
- Ferrous Chloride
- Hexane
- Hydrochloric Acid
- Hydrofluoric Acid
- Hydrofluorosilicic Acid
- Hydrogen Cyanide
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Hydrofluoric Acid
- Hypochlorous Acid
- Isopropyl Acetate
- Liquid Argon
- Liquid Nitrogen
- Liquid Oxygen
- Maleic Anhydride
- MDI
- Methanol
- Methyl Chloride
- Methyl Ethyl Ketone
- Methyl Methacrylate
- Methyl Isocyanate
- Molten Sulphur
- Nitric Acid
- Oleum
- Phenol
- Phosphoric Acid
- Phosphorus Oxychloride
- Phosphorus Trichloride
- Polypropylene
- Renewable Diesel
- Sodium Cyanide
- Sodium Hydroxide
- Sodium Hypochlorite
- Styrene Monomer
- Sulfuric Acid
- Sulfur Dioxide
- Titanium Tetrachloride
- Toluene
- Toluene Diisocyanate
- Turpenitne
- UAN (Urea Ammonium Nitrate)
- UREA
- Vinyl Acetate
- Vinyl Chloride
- Xylene
- Zinc Chloride
- Agro-Chemical
- Specialty Chemical
- Petrochemical

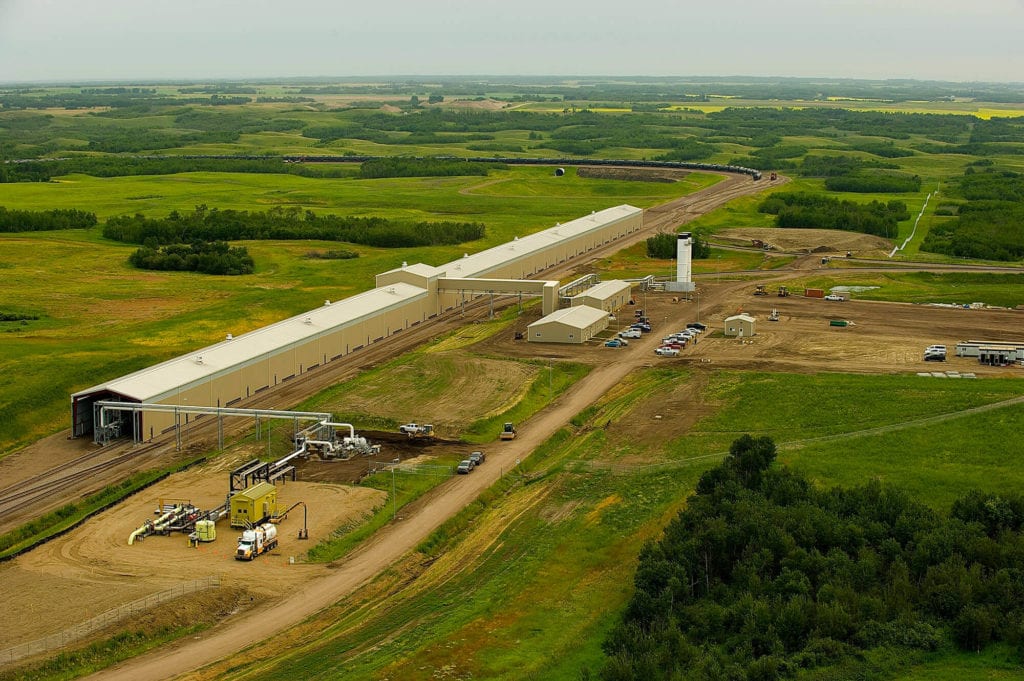
North America’s largest loading terminal
World-leading designer, manufacturer, and installer of truck and railcar loading platforms
As one of the primary railcar loading points, Hardisty is one of the major crude oil hubs in North America and a major origination point of pipelines that export to the United States. SCS was asked to supply and construct a SafeRack crude oil loadout terminal spanning nearly half a mile. The USD Hardisty terminal can load up to two 120-railcar unit trains per day and consists of a fixed loading rack with 62 railcar loading positions enclosed, separate control, operator, and mechanical buildings, as well as a unit train staging area and loop tracks capable of holding multiple unit trains simultaneously. SCS also supplied and installed boom-supported loading arms with supply and vapor management systems.

Quick Quote 866-761-7225
LET US DESIGN YOUR SOLUTION TODAY
Our innovative tools provide 3D visualizations and accurate quotes in minutes.
Get Help NowOrder Now 866-761-7225
Questions or Need a Quote?
Chat live with a knowledgeable and friendly safety expert now.

Bob Kashtan
Located in South Carolina

Joey Robinson
Located in South Carolina

Caelin Lacy
Located in South Carolina

Katie Kelly
Located in South Carolina

Amber Graham
Located in South Carolina
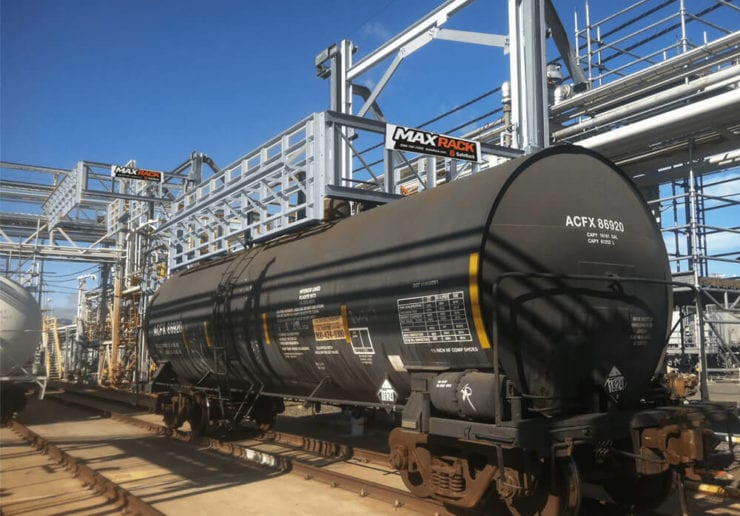
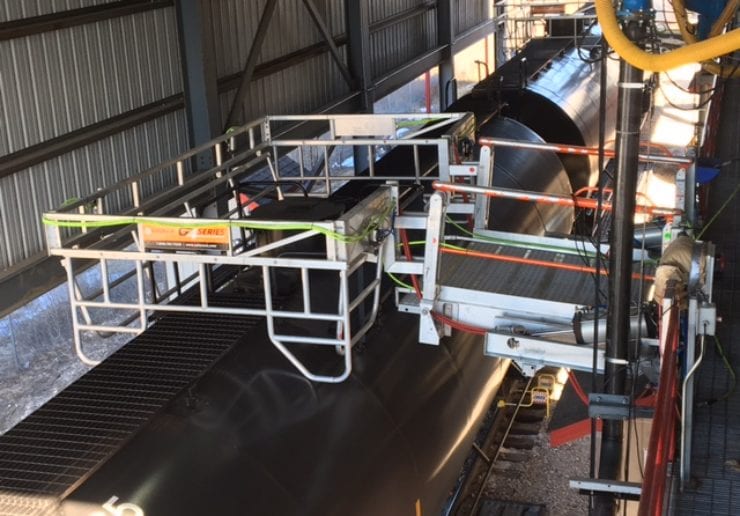
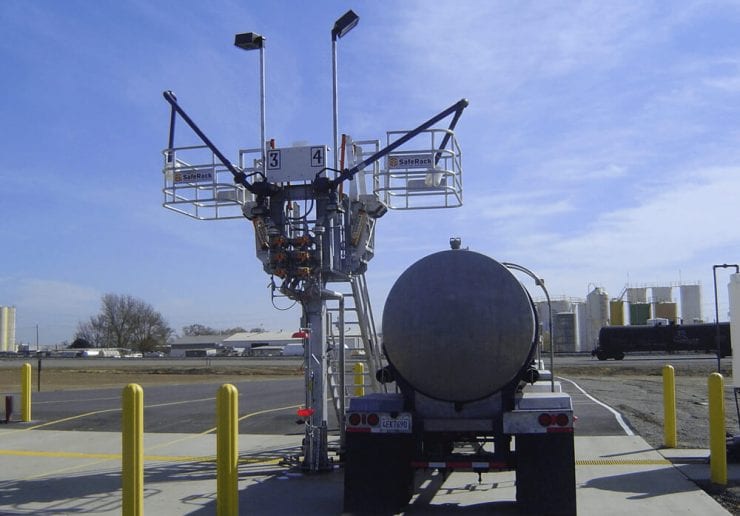


























 As an alternative to our two and four-rail safety cages, some customers prefer our MAXRack elevating safety cages. The ultimate fall prevention solution engineered to keep operators safe and productive. Designed for both trucks or railcars, and available in multiple cage lengths and widths. Safe, durable, and easy to use. MAXRack is built rock-solid with galvanized steel column supports and lifting arms (cages can be Aluminum, Galvanized, or Stainless Steel depending on application) Available in two power options – Pneumatic Air Drive and Electric Drive (Explosion and Non-Explosion Proof).
As an alternative to our two and four-rail safety cages, some customers prefer our MAXRack elevating safety cages. The ultimate fall prevention solution engineered to keep operators safe and productive. Designed for both trucks or railcars, and available in multiple cage lengths and widths. Safe, durable, and easy to use. MAXRack is built rock-solid with galvanized steel column supports and lifting arms (cages can be Aluminum, Galvanized, or Stainless Steel depending on application) Available in two power options – Pneumatic Air Drive and Electric Drive (Explosion and Non-Explosion Proof).



 YellowGate Safety Gates
YellowGate Safety Gates